Getting Started
This page provides a step-by-step guide to quickly get started with AdminForth using the adminforth CLI.
You will learn how to set up a new project using the adminforth create-app command and explore AdminForth’s fundamentals.
👆 For setup example without CLI check out Hello World without CLI
Prerequisites
AdminForth requires Node v20 or higher. If you’re on a different version, you can switch or install using:
nvm install 20
nvm alias default 20
nvm use 20
Creating an AdminForth Project
The recommended way to get started with AdminForth is via the create-app CLI, which scaffolds a basic fully functional back-office application. Apart boilerplate it creates one resource for users management.
You can provide options directorly:
npx adminforth create-app --app-name myadmin --db "sqlite://.db.sqlite"
Or omit them to be prompted interactively:
npx adminforth create-app
Once the project is created, navigate into its directory:
cd myadmin # or any other name you provided
CLI options:
--app-name- name for your project. Used inpackage.json,index.tsbranding, etc. Default value:adminforth-app.--db- database connection string. Currently PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SQLite, MySQL, Clickhouse are supported. Default value:sqlite://.db.sqlite
☝️ Database Connection String format:
Format is
<scheme>://<username>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<database>. Examples:
- SQLite —
sqlite://.db.sqlite. If database not yet exists it will be created- PostgreSQL —
postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname- MongoDB —
mongodb://localhost:27017/dbname- Clickhouse —
clickhouse://localhost:8123/dbname- MySQL —
mysql://user:password@localhost:3306/dbname
Understand the generated Project Structure
The CLI will create boilerplate files and folders in your current directory and install dependencies. A typical layout looks like this:
myadmin/
├── custom
│ ├── assets/ # Static assets like images, fonts, etc.
│ ├── package.json # For any custom npm packages you will use in Vue files
│ └── tsconfig.json # Tsconfig for Vue project (adds completion for AdminForth core components)
├── resources
│ └── adminuser.ts # Example resource file for users management
├── schema.prisma # Prisma schema file for database schema
├── index.ts # Main entry point: configures AdminForth & starts the server
├── package.json # Project dependencies
├── tsconfig.json # TypeScript configuration
├── .env # Env vars like tokens, secrets that should not be in version control
├── .env.local # General local environment variables
└── .gitignore
Initial Migration & Future Migrations
☝️ CLI creates Prisma schema file for managing migrations in relational databases, however you are not forced to use it. Instead you are free to use your favourite or existing migration tool. In this case just ignore generated prisma file, and don't run migration command which will be suggested by CLI. However you have to ensure that your migration tool will generate required table
adminuserwith same fields and types for Admin Users resource to implmenet BackOffice authentication.
CLI will suggest you a command to initialize the database with Prisma:
npm run makemigration -- --name init
This will create a migration file in migrations and apply it to the database.
In future, when you need to add new resources, you need to modify schema.prisma (add models, change fields, etc.). After doing any modification you need to create a new migration using next command:
npm run makemigration -- --name init ; npm run migrate:local
Other developers need to pull migration and run npm run migrateLocal to apply any unapplied migrations.
Run the Server
Now you can run your app:
npm start
Open http://localhost:3500 in your browser and (default credentials are adminforth/adminforth if you haven’t changed them).
AdminForth Basic Philosophy
AdminForth connects to existing databases and provides a back-office for managing data including CRUD operations, filtering, sorting, and more.
Database can be already created by using any database management tool, ORM or migrator.
AdminForth itself never modifies database schema, does not add columns or new tables. However for those who have no own migration managment AdminForth CLI suggests using Prisma. This allows to provide simple and reliable schema management for standalone projects which have no DB yet.
If you already have a database, you pass a connection string to AdminForth and define resources(tables) and describe columns you would like to see in back-office. For most DBs AdminForth can "discover" column types and constraints (e.g. max-length) by connecting to DB. However you can redefine them in AdminForth configuration. Type and constraints definition in AdminForth resource are take precedence over DB schema.
Also in AdminForth you can define in "Vue" way:
- how each field will be rendered
- create own pages e.g. Dashboard using AdminForth Components Library (AFCL) or any other Vue componetns.
- insert injections into standard pages (e.g. add diagram to list view)
Adding an apartments Model
So far, our freshly generated AdminForth project includes a default adminuser model and a corresponding adminuser resource.
Let’s expand our app to suport managment of apartments model. Adding new resource will involve next steps:
- Add a new Prisma model to your
schema.prisma. - Run a Prisma migration to update your database schema.
- Create a corresponding resource in the
resources/folder. - Register the new resource in
index.tsand see it in your AdminForth back-office.
Please note that steps 1 and 2 are compleatly independent from 3 and 4, so you can make them with any other way then Prisma.
Step 1. Define the apartments Model in schema.prisma
Open schema.prisma in your project root and add a new model for apartments:
...
model apartments {
id String @id
created_at DateTime?
title String
square_meter Float?
price Decimal
number_of_rooms Int?
description String?
country String?
listed Boolean
realtor_id String?
}
Step 2. Create and Apply the Migration
Run the following command to create a new migration:
npm run makemigration -- --name add-apartments ; npm run migrate:local
Step3. Create the apartments resource
Create a new file apartments.ts in the resources/ folder:
import { AdminForthDataTypes, AdminForthResourceInput } from 'adminforth';
export default {
dataSource: 'maindb',
table: 'apartments',
resourceId: 'aparts', // resourceId is defaulted to table name but you can redefine it like this e.g.
// in case of same table names from different data sources
label: 'Apartments', // label is defaulted to table name but you can change it
recordLabel: (r) => `🏡 ${r.title}`,
columns: [
{
name: 'id',
type: AdminForthDataTypes.STRING,
label: 'Identifier', // if you wish you can redefine label, defaulted to uppercased name
showIn: { // show column in filter and in show page
list: false,
edit: false,
create: false,
},
primaryKey: true,
fillOnCreate: ({ initialRecord, adminUser }) => Math.random().toString(36).substring(7), // called during creation to generate content of field, initialRecord is values user entered, adminUser object of user who creates record
},
{
name: 'title',
required: true,
showIn: { all: true }, // all available options
type: AdminForthDataTypes.STRING,
maxLength: 255, // you can set max length for string fields
minLength: 3, // you can set min length for string fields
},
{
name: 'created_at',
type: AdminForthDataTypes.DATETIME,
allowMinMaxQuery: true,
showIn: { create: false },
fillOnCreate: ({ initialRecord, adminUser }) => (new Date()).toISOString(),
},
{
name: 'price',
inputSuffix: 'USD', // you can add a suffix to an input field that will be displayed when creating or editing records
allowMinMaxQuery: true, // use better experience for filtering e.g. date range, set it only if you have index on this column or if you sure there will be low number of rows
editingNote: 'Price is in USD', // you can put a note near field on editing or creating page
},
{
name: 'square_meter',
label: 'Square',
allowMinMaxQuery: true,
minValue: 1, // you can set min /max value for number columns so users will not be able to enter more/less
maxValue: 1000,
},
{
name: 'number_of_rooms',
allowMinMaxQuery: true,
enum: [
{ value: 1, label: '1 room' },
{ value: 2, label: '2 rooms' },
{ value: 3, label: '3 rooms' },
{ value: 4, label: '4 rooms' },
{ value: 5, label: '5 rooms' },
],
},
{
name: 'description',
sortable: false,
showIn: { list: false },
},
{
name: 'country',
enum: [{
value: 'US',
label: 'United States'
}, {
value: 'DE',
label: 'Germany'
}, {
value: 'FR',
label: 'France'
}, {
value: 'GB',
label: 'United Kingdom'
}, {
value: 'NL',
label: 'Netherlands'
}, {
value: 'IT',
label: 'Italy'
}, {
value: 'ES',
label: 'Spain'
}, {
value: 'DK',
label: 'Denmark'
}, {
value: 'PL',
label: 'Poland'
}, {
value: 'UA',
label: 'Ukraine'
}, {
value: null,
label: 'Not defined'
}],
},
{
name: 'listed',
required: true, // will be required on create/edit
},
{
name: 'realtor_id',
foreignResource: {
resourceId: 'adminuser',
searchableFields: ["id", "email"], // fields available for search in filter
}
}
],
options: {
listPageSize: 12,
allowedActions: {
edit: true,
delete: true,
show: true,
filter: true,
},
},
} as AdminForthResourceInput;
Step 4. Register the apartments Resource
Open index.ts in your project root and import the new resource:
...
import apartmentsResource from "./resources/apartments.js";
...
export const admin = new AdminForth({
...
resources: [
usersResource,
apartmentsResource,
],
menu: [
{
label: 'Core',
icon: 'flowbite:brain-solid',
open: true,
children: [
{
homepage: true,
label: 'Apartments',
icon: 'flowbite:home-solid',
resourceId: 'aparts',
},
]
},
{ type: 'gap' },
{ type: 'divider' },
{
type: 'heading',
label: 'SYSTEM'
},
{
label: 'Users',
...
}
],
...
});
Generating fake appartments
async function seedDatabase() {
if (await admin.resource('aparts').count() > 0) {
return
}
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
await admin.resource('aparts').create({
id: `${i}`,
title: `Apartment ${i}`,
square_meter: (Math.random() * 100).toFixed(1),
price: (Math.random() * 10000).toFixed(2),
number_of_rooms: Math.floor(Math.random() * 4) + 1,
description: 'Next gen apartments',
created_at: (new Date(Date.now() - Math.random() * 60 * 60 * 24 * 14 * 1000)).toISOString(),
listed: i % 2 == 0,
country: `${['US', 'DE', 'FR', 'GB', 'NL', 'IT', 'ES', 'DK', 'PL', 'UA'][Math.floor(Math.random() * 10)]}`
});
};
};
if (fileURLToPath(import.meta.url) === path.resolve(process.argv[1])) {
...
admin.discoverDatabases().then(async () => {
if (!await admin.resource('adminuser').get([Filters.EQ('email', 'adminforth')])) {
await admin.resource('adminuser').create({
email: 'adminforth',
password_hash: await AdminForth.Utils.generatePasswordHash('adminforth'),
role: 'superadmin',
});
}
await seedDatabase();
});
This will create records during first launch. Now you should see:
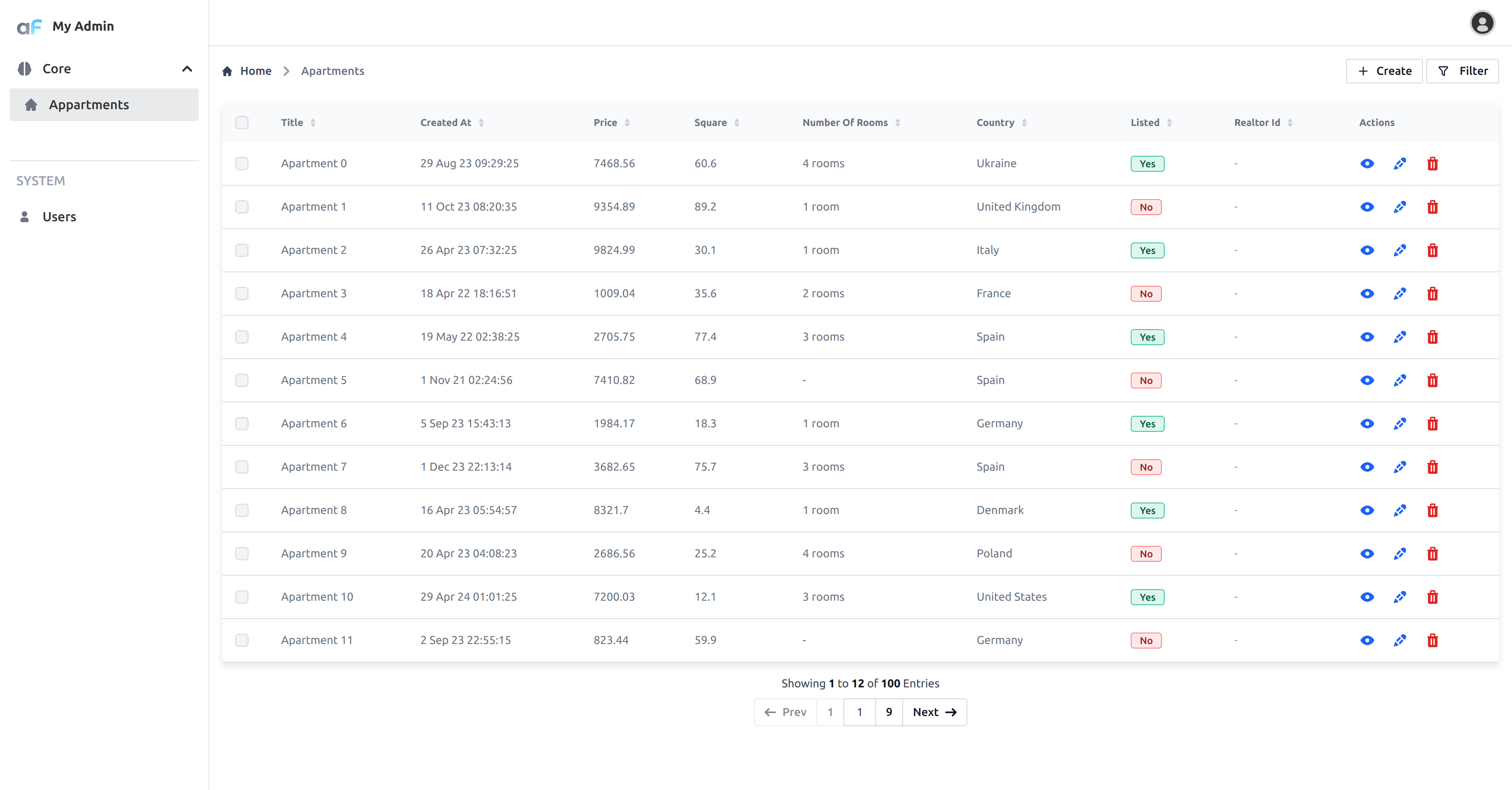
Feel free to play with the data, add more fields, and customize the UI to your liking.